A Comparison of the neural correlates that underlie rule-based and information-integration category learning
| dc.contributor.author | Carpenter, Kathryn | |
| dc.contributor.author | Wills, Andy | |
| dc.contributor.author | Benattayallah, A | |
| dc.contributor.author | Milton, F | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2016-07-13T09:50:25Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2016-07-13T09:50:25Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2016-10 | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1065-9471 | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1097-0193 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10026.1/5050 | |
| dc.description.abstract |
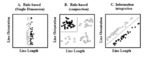
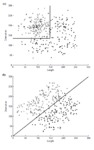
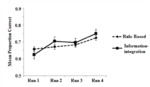
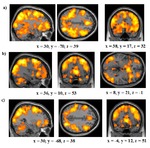
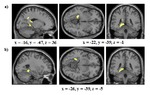
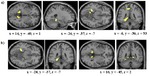
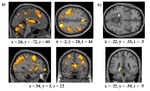
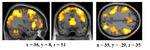
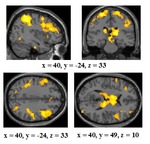
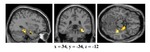
The influential competition between verbal and implicit systems (COVIS) model proposes that category learning is driven by two competing neural systems-an explicit, verbal, system, and a procedural-based, implicit, system. In the current fMRI study, participants learned either a conjunctive, rule-based (RB), category structure that is believed to engage the explicit system, or an information-integration category structure that is thought to preferentially recruit the implicit system. The RB and information-integration category structures were matched for participant error rate, the number of relevant stimulus dimensions, and category separation. Under these conditions, considerable overlap in brain activation, including the prefrontal cortex, basal ganglia, and the hippocampus, was found between the RB and information-integration category structures. Contrary to the predictions of COVIS, the medial temporal lobes and in particular the hippocampus, key regions for explicit memory, were found to be more active in the information-integration condition than in the RB condition. No regions were more activated in RB than information-integration category learning. The implications of these results for theories of category learning are discussed. Hum Brain Mapp 37:3557-3574, 2016. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. | |
| dc.format.extent | 3557-3574 | |
| dc.format.medium | Print-Electronic | |
| dc.language | en | |
| dc.language.iso | en | |
| dc.publisher | Wiley | |
| dc.subject | magnetic resonance imaging | |
| dc.subject | learning | |
| dc.subject | verbal | |
| dc.subject | hippocampus | |
| dc.subject | parahippocampal gyrus | |
| dc.subject | caudate nucleus | |
| dc.title | A Comparison of the neural correlates that underlie rule-based and information-integration category learning | |
| dc.type | journal-article | |
| dc.type | Comparative Study | |
| dc.type | Journal Article | |
| dc.type | Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't | |
| plymouth.author-url | https://www.webofscience.com/api/gateway?GWVersion=2&SrcApp=PARTNER_APP&SrcAuth=LinksAMR&KeyUT=WOS:000383864500014&DestLinkType=FullRecord&DestApp=ALL_WOS&UsrCustomerID=11bb513d99f797142bcfeffcc58ea008 | |
| plymouth.issue | 10 | |
| plymouth.volume | 37 | |
| plymouth.publication-status | Published | |
| plymouth.journal | Human Brain Mapping | |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1002/hbm.23259 | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Admin Group - REF | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Admin Group - REF/REF Admin Group - FoH | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Faculty of Health | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Faculty of Health/School of Psychology | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/REF 2021 Researchers by UoA | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/REF 2021 Researchers by UoA/UoA04 Psychology, Psychiatry and Neuroscience | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/REF 2021 Researchers by UoA/UoA17 Business and Management Studies | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Research Groups | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Research Groups/Institute of Health and Community | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Users by role | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Users by role/Academics | |
| dc.publisher.place | United States | |
| dcterms.dateAccepted | 2016-05-02 | |
| dc.rights.embargodate | 2017-5-20 | |
| dc.identifier.eissn | 1097-0193 | |
| dc.rights.embargoperiod | 12 months | |
| rioxxterms.versionofrecord | 10.1002/hbm.23259 | |
| rioxxterms.licenseref.uri | http://www.rioxx.net/licenses/under-embargo-all-rights-reserved | |
| rioxxterms.licenseref.startdate | 2016-10 | |
| rioxxterms.type | Journal Article/Review | |
| plymouth.oa-location | https://ore.exeter.ac.uk/repository/handle/10871/21390 |