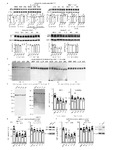
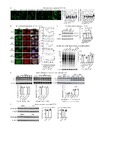
Allele-selective lowering of mutant HTT protein by HTT–LC3 linker compounds
| dc.contributor.author | Li, Z | |
| dc.contributor.author | Wang, C | |
| dc.contributor.author | Wang, Z | |
| dc.contributor.author | Zhu, C | |
| dc.contributor.author | Li, J | |
| dc.contributor.author | Sha, T | |
| dc.contributor.author | Ma, L | |
| dc.contributor.author | Gao, C | |
| dc.contributor.author | Yang, Y | |
| dc.contributor.author | Sun, Y | |
| dc.contributor.author | Wang, J | |
| dc.contributor.author | Sun, X | |
| dc.contributor.author | Lu, C | |
| dc.contributor.author | Difiglia, M | |
| dc.contributor.author | Mei, Y | |
| dc.contributor.author | Ding, C | |
| dc.contributor.author | Luo, Shouqing | |
| dc.contributor.author | Dang, Y | |
| dc.contributor.author | Ding, Y | |
| dc.contributor.author | Fei, Y | |
| dc.contributor.author | Lu, B | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2019-11-14T09:18:29Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2019-11-14T09:18:29Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2019-10-30 | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 0028-0836 | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1476-4687 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10026.1/15145 | |
| dc.description.abstract |
Accumulation of mutant proteins is a major cause of many diseases (collectively called proteopathies), and lowering the level of these proteins can be useful for treatment of these diseases. We hypothesized that compounds that interact with both the autophagosome protein microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B light chain 3 (LC3)1 and the disease-causing protein may target the latter for autophagic clearance. Mutant huntingtin protein (mHTT) contains an expanded polyglutamine (polyQ) tract and causes Huntington's disease, an incurable neurodegenerative disorder2. Here, using small-molecule-microarray-based screening, we identified four compounds that interact with both LC3 and mHTT, but not with the wild-type HTT protein. Some of these compounds targeted mHTT to autophagosomes, reduced mHTT levels in an allele-selective manner, and rescued disease-relevant phenotypes in cells and in vivo in fly and mouse models of Huntington's disease. We further show that these compounds interact with the expanded polyQ stretch and could lower the level of mutant ataxin-3 (ATXN3), another disease-causing protein with an expanded polyQ tract3. This study presents candidate compounds for lowering mHTT and potentially other disease-causing proteins with polyQ expansions, demonstrating the concept of lowering levels of disease-causing proteins using autophagosome-tethering compounds. | |
| dc.format.extent | 203-209 | |
| dc.format.medium | Print-Electronic | |
| dc.language | en | |
| dc.language.iso | en | |
| dc.publisher | Springer Science and Business Media LLC | |
| dc.rights | Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International | |
| dc.rights | Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International | |
| dc.rights | Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International | |
| dc.rights | Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International | |
| dc.rights | Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International | |
| dc.rights | Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International | |
| dc.rights | Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International | |
| dc.rights | Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International | |
| dc.rights | Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International | |
| dc.rights | Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International | |
| dc.rights | Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International | |
| dc.rights | Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International | |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ | |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ | |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ | |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ | |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ | |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ | |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ | |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ | |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ | |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ | |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ | |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ | |
| dc.subject | Alleles | |
| dc.subject | Animals | |
| dc.subject | Ataxin-3 | |
| dc.subject | Autophagosomes | |
| dc.subject | Autophagy | |
| dc.subject | Disease Models, Animal | |
| dc.subject | Drosophila Proteins | |
| dc.subject | Drosophila melanogaster | |
| dc.subject | Drug Evaluation, Preclinical | |
| dc.subject | Female | |
| dc.subject | Humans | |
| dc.subject | Huntingtin Protein | |
| dc.subject | Male | |
| dc.subject | Mice | |
| dc.subject | Microtubule-Associated Proteins | |
| dc.subject | Mutant Proteins | |
| dc.subject | Mutation | |
| dc.subject | Neurons | |
| dc.subject | Peptides | |
| dc.subject | Phenotype | |
| dc.subject | Reproducibility of Results | |
| dc.title | Allele-selective lowering of mutant HTT protein by HTT–LC3 linker compounds | |
| dc.type | journal-article | |
| dc.type | Journal Article | |
| dc.type | Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't | |
| plymouth.author-url | https://www.webofscience.com/api/gateway?GWVersion=2&SrcApp=PARTNER_APP&SrcAuth=LinksAMR&KeyUT=WOS:000496159900062&DestLinkType=FullRecord&DestApp=ALL_WOS&UsrCustomerID=11bb513d99f797142bcfeffcc58ea008 | |
| plymouth.issue | 7781 | |
| plymouth.volume | 575 | |
| plymouth.publication-status | Published | |
| plymouth.journal | Nature | |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1038/s41586-019-1722-1 | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Faculty of Health | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Faculty of Health/Peninsula Medical School | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/REF 2021 Researchers by UoA | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/REF 2021 Researchers by UoA/UoA01 Clinical Medicine | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Research Groups | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Research Groups/Institute of Translational and Stratified Medicine (ITSMED) | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Research Groups/Institute of Translational and Stratified Medicine (ITSMED)/CBR | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Users by role | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Users by role/Academics | |
| plymouth.organisational-group | /Plymouth/Users by role/Researchers in ResearchFish submission | |
| dc.publisher.place | England | |
| dcterms.dateAccepted | 2019-09-24 | |
| dc.rights.embargodate | 2020-4-29 | |
| dc.identifier.eissn | 1476-4687 | |
| dc.rights.embargoperiod | Not known | |
| rioxxterms.versionofrecord | 10.1038/s41586-019-1722-1 | |
| rioxxterms.licenseref.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ | |
| rioxxterms.licenseref.startdate | 2019-10-30 | |
| rioxxterms.type | Journal Article/Review | |
| plymouth.funder | Tackling autophagy and apoptosis for the potential therapy of Huntington's Disease::MRC | |
| plymouth.funder | Tackling autophagy and apoptosis for the potential therapy of Huntington's Disease::MRC |